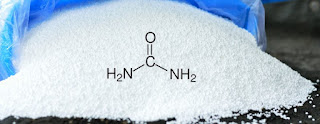
Urea, a compound containing nitrogen, carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen, plays a pivotal role in agriculture by serving as a potent fertilizer. Its significance in promoting plant growth and increasing crop yields has made it a cornerstone in modern farming practices.
 |
| Manufacture of Urea |
Historical Background
- Discovery of Urea
The journey of urea dates back to the early 19th century when German chemist Friedrich Wöhler first synthesized it in 1828. This groundbreaking discovery shattered the belief that organic compounds could only be derived from living organisms, marking a revolutionary moment in chemistry.
- Early Manufacturing Methods
In its initial stages, urea was primarily obtained through natural sources like urine. However, as demand grew, innovative methods emerged, paving the way for more efficient production processes.
Urea Industry in Pakistan
In Pakistan, the urea industry plays a pivotal role in supporting the country's agricultural sector. Pakistan has several urea manufacturing plants, contributing significantly to the production of nitrogen-rich fertilizers. These plants, operated by various companies, help meet the growing demand for urea in agriculture, ensuring sustainable crop yields and food security. The industry's presence underscores its importance in fostering agricultural growth and economic development in Pakistan. For the latest and more detailed information, it's advisable to check current sources.
Modern Urea Production
- Chemical Process
Today, urea is predominantly manufactured through a chemical process known as the Haber-Bosch synthesis. This method combines ammonia and carbon dioxide to produce urea, highlighting the remarkable progress in industrial chemistry.
- Key Ingredients
The key ingredients in urea production include ammonia and carbon dioxide, sourced from various industrial processes. The precise combination and controlled conditions are crucial for optimizing the yield and quality of urea.
- Industrial Scale Production
With advancements in technology, urea is now produced on an industrial scale. Large manufacturing plants utilize cutting-edge equipment and processes to meet the ever-growing demand for this essential agricultural input.
Applications of Urea
- Agricultural Use
 |
| Manufacture of Urea |
The primary application of urea lies in agriculture, where it serves as a nitrogen-rich fertilizer. Its solubility and high nitrogen content make it an ideal choice for promoting healthy plant growth and maximizing crop yields.
- Industrial Applications
Beyond agriculture, urea finds application in various industrial processes, including plastics manufacturing and automotive systems. Its versatility extends its utility beyond the realms of farming.
Environmental Impact
- Nitrogen Pollution
While urea is a boon for agriculture, its excessive use can contribute to nitrogen pollution, adversely affecting water bodies and ecosystems. Striking a balance between agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability becomes imperative.
- Mitigation Strategies
Addressing the environmental impact of urea involves adopting mitigation strategies such as precision agriculture, improved application techniques, and the development of nitrogen-efficient crops.
Challenges in Urea Manufacturing
- Energy Consumption
One of the significant challenges in urea manufacturing is the high energy consumption associated with the production process. Research and development efforts focus on creating energy-efficient methods to minimize environmental footprint.
- Environmental Regulations
Stringent environmental regulations pose challenges to urea manufacturers, necessitating the adoption of cleaner and greener technologies to meet compliance standards.
Innovations in Urea Production
- Green Technologies
In the quest for sustainability, the industry is witnessing the emergence of green technologies in urea production. Innovations aim to reduce carbon footprint, energy consumption, and overall environmental impact.
- Sustainable Practices
Adopting sustainable practices, such as utilizing renewable energy sources and optimizing resource utilization, represents a promising path towards a more eco-friendly urea manufacturing process.
Future Trends of Urea
- Advancements in Urea Synthesis
Ongoing research and development promise advancements in urea synthesis, exploring novel catalysts and process optimizations that enhance efficiency and reduce environmental repercussions.
- Market Projections
The urea market is poised for growth, driven by increasing global demand for food production. Market projections indicate a steady rise, with a focus on sustainable and eco-friendly urea production methods.
FAQs
Is urea only used in agriculture?
- No, urea has diverse applications, including industrial uses in manufacturing and automotive systems.
What are the environmental challenges associated with urea use?
- Urea can contribute to nitrogen pollution, impacting water bodies. Mitigation strategies are crucial to address these challenges.
How has urea production evolved over time?
- Urea production has transitioned from early methods relying on natural sources to modern, chemical processes on an industrial scale.
What are the key ingredients in urea production?
- The main ingredients are ammonia and carbon dioxide, sourced from industrial processes.
What is the future outlook for the urea market?
- The urea market is expected to grow, with a focus on sustainable production methods and technological advancements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the manufacture of urea has evolved from historical methods to sophisticated, large-scale industrial processes. Balancing the crucial role of urea in agriculture with environmental concerns requires continuous innovation and a commitment to sustainable practices.




