Charle's Law is a fundamental principle in physics and chemistry that describes how gases tend to expand when heated. Named after Jacques Charles, a French scientist, this law provides insights into the behavior of gases under changing temperature conditions.
 |
| Charle's Law |
Definition of Charle's Law
Charle's Law states that, at constant pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature. In other words, as the temperature of a gas increases, so does its volume, and vice versa, as long as the pressure remains constant.
What is Charle's Law?
Charle's law, commonly known as the law of volumes, provides a thorough explanation of how gas expands as temperature rises. On the other hand, a drop in temperature will cause a drop in volume.
From the above statement, we can write this as follows when comparing a substance under two distinct conditions:
T2/T1 = V2/V1
OR
V1T2 = V2T1
The aforementioned equation shows that the volume of the gas increases proportionately with an increase in absolute temperature.
To put it another way, the ideal gas law applies specifically to Charle's law. Ideal gases that are maintained at constant pressure but whose temperature and volume fluctuate are covered by the law.
We have learnt Boyle's Law.
Mathematical Expression
The mathematical expression of Charle's Law is straightforward:
V∝T
Where:
- V is the volume of the gas,
- T is its absolute temperature (measured in Kelvin).
This equation emphasizes the direct proportionality between volume and temperature.
Derivations
The foundation of Charle's Law lies in the kinetic theory of gases. As gases heat up, the average kinetic energy of their particles increases, leading to more energetic and spaced-out movement. This results in an expansion of the gas volume.
Graphical Explanation
A graphical representation helps visualize Charle's Law. A graph plotting volume against temperature at constant pressure produces a straight line. This line has a positive slope, indicating the direct proportionality between volume and temperature.
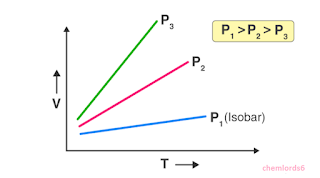 |
Graphical Explanation |
FAQs about Charle's Law
Can Charle's Law be applied to all gases?
Yes, Charle's Law is applicable to all ideal gases under constant pressure.
Why is temperature measured in Kelvin in Charle's Law?
The Kelvin scale is used to ensure an absolute temperature scale, as it starts from absolute zero, the point at which particles have minimum kinetic energy.
How does Charle's Law relate to everyday experiences?
Think of inflating a balloon: as you blow hot air into it, the volume increases, demonstrating Charle's Law in action.
Conclusion
Charle's Law provides a fundamental understanding of how gases respond to changes in temperature. Its simplicity and applicability make it a cornerstone in the study of thermodynamics. By grasping this principle, we gain valuable insights into the behavior of gases in various practical scenarios.
In conclusion, Charle's Law serves as a key building block in the comprehension of gas behavior, offering a simple yet powerful tool for scientists and students alike.
.jpg)
.jpg)




